Genclis is a privately held biotechnology company, based in Nancy, France.
It focuses on alternate RNA derived therapeutics.
Genclis has developed a technology platform based on its discovery of Transcription Infidelity (“TI”), causing gaps in mRNA. Proteins translated from these mRNA are designated TI proteins and hold specific immunological properties.
What is Transcription Infidelity?
Revolutionizing immunology one indication at a time.
Pipeline
Our current fields of drug development
Discovery
Preclinical
Phase I
Phase 2
Phase 3

Veterinary Allergy
Human Allergy

Severe Covid

Type I Diabetes

Lou Gehrig’s disease
- 70%
- 30%
- 30%
- 10%
- 10%
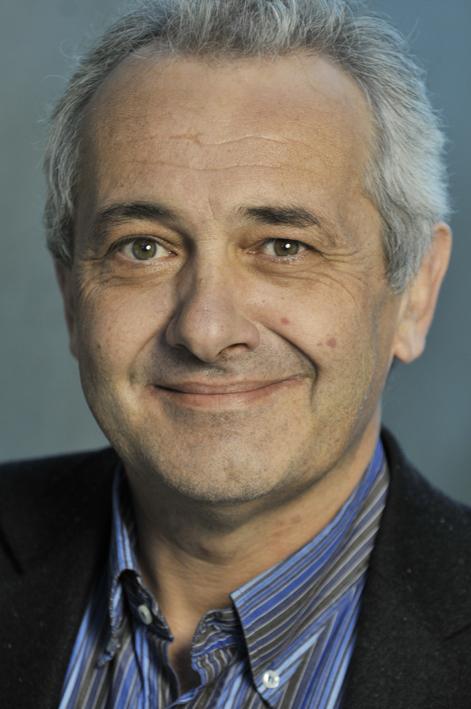

Word from our CEO

Welcome to Genclis!
I am proud to lead a team of highly skilled and enthusiastic scientists to tackle some of the most critical battles modern medicine faces.
Patients first
At Genclis, curing people is our main mission. My life’s goal has been to alleviate unnecessary suffering and pain. We have achieved major breakthroughs in the veterinary field and we are on the verge of victories for human medicine.
Driven by Science
Genclis employees all share a passion for science. Our job is to make sense of what has none.
This passion enabled us to discover a novel molecular biology mechanism, charter its rules, and find its role in the education of the immune system. Beyond immunology, our goal is to rule immunity. Our technology elicits, enhances, or tames antibodies.
Baby steps
Genclis explores unknown territories and de-risks its therapeutic solutions with convergent, highly robust preclinical data. As a small company with limited resources, we carefully arbitrage our many opportunities.
Company stewards
We are faithful stewards of the funds entrusted to us by our shareholders. Our financial statements reflect our stability. This unconventional biotech business model may be slow but it is steady.
Bernard Bihain, Co-founder and CEO
Bioinformatics
“We’re dedicated to improving patient outcomes with reliable AI-Powered technology and meaningful collaboration with biopharma, laboratories, and clinicians — aiming to provide patients with access to accurate diagnoses and effective treatments.”

Incorporation

Patents granted

Staff
PhDs / MDs
Publications
Publications
Transcriptional frameshifts contribute to protein allergenicity
Thouvenot B, Roitel O, Tomasina J, Hilselberger B, Richard C, Jacquenet S, Codreanu-Morel F, Morisset M, Kanny G, Beaudouin E, Delebarre-Sauvage C, Olivry T, Favrot C, Bihain B.- Journal of Clinical Investigation 2020 Jul.
Lipolysis stimulated lipoprotein receptor: a novel molecular link between hyperlipidemia, weight gain, and atherosclerosis in mice
Yen FT, Roitel O, Bonnard L, Notet V, Pratte D, Stenger C, Magueur E, Bihain BE. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2008 Sep 12
Nonrandom variations in human cancer ESTs indicate that mRNA heterogeneity increases during carcinogenesis
Marie Brulliard, Dalia Lorphelin, Olivier Collignon, Walter Lorphelin, Benoit Thouvenot, Emmanuel Gothié, Sandrine Jacquenet, Virginie Ogier, Olivier Roitel,Jean-Marie Monnez, Pierre Vallois, Frances T Yen, Olivier Poch, Marc Guenneugues, Gilles Karcher, Pierre Oudet, Bernard E Bihain – Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences May 2007
